Understanding the Climate Imperative
Climate change has emerged as the defining challenge of our era. To limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels – the threshold identified by the IPCC to prevent catastrophic impacts – achieving Net Zero Emissions by 2050 has become the critical global target.
Key Definition:
Net Zero requires balancing anthropogenic greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions with carbon removal through natural and engineered sinks, creating equilibrium between atmospheric inputs and outputs.
The Carbon Budget Reality

| Metric | Value | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Remaining Carbon Budget | 500 Gt CO₂ | Maximum allowable emissions to stay below 1.5°C |
| 2019 Global Emissions | 59 ±6.6 Gt CO₂ | Increasing ~1.1% annually |
| Budget Depletion Timeline | <10 years | At current emission rates |
IPCC Pathways Demand:
- 45% GHG reduction by 2030
- Net Zero before 2050
Business Drivers for Net Zero Action
1. Supply Chain Requirements

Global corporations are cascading mandates through value chains:
MEITU Study:
– Achieved operational carbon neutrality (2020)
– Requires 100% supply chain neutrality by 2030
– 200+ suppliers (70% manufacturing spend) committed to 100% renewable energy
2. Carbon Border Mechanisms
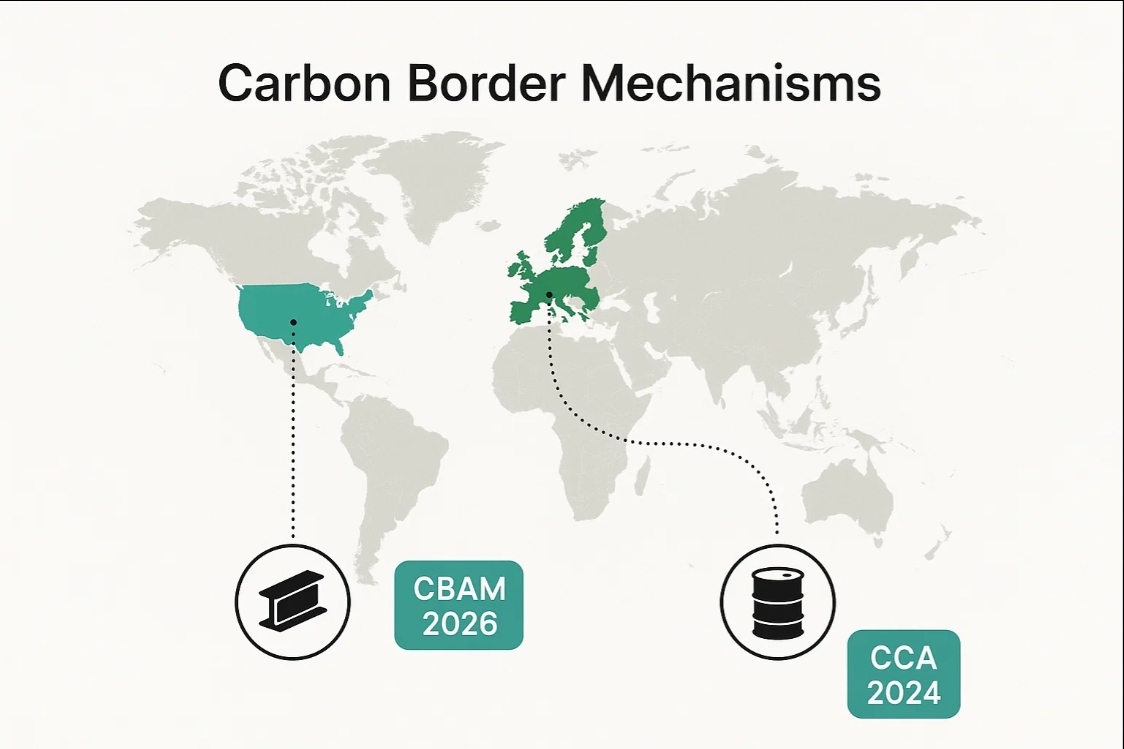
EU Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM):
- 2023: Reporting begins
- 2026: Full implementation
- Covers steel, cement, fertilizers, electricity
- Non-compliance penalty: 20-35% cost increase
US Clean Competition Act (CCA):
- Proposed 2024 implementation
- $55/ton fee on carbon-intensive imports
Implementation Roadmap
Four-Phase Approach
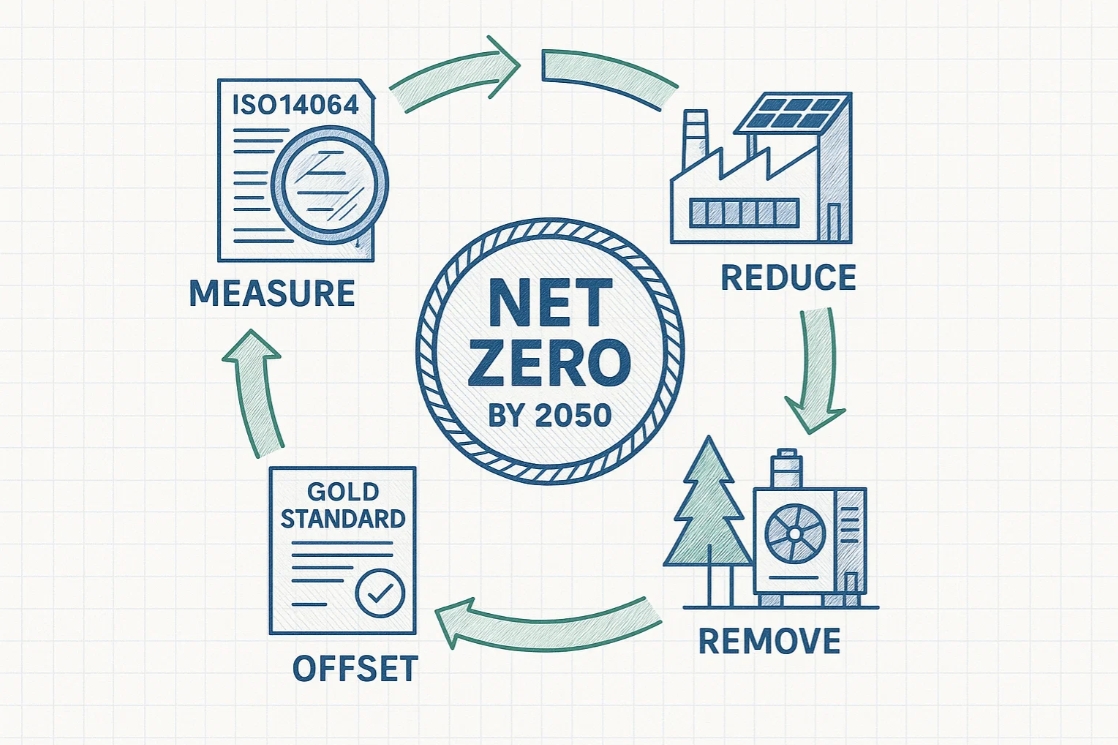
1. Carbon Footprint Verification
- Conduct ISO 14064/14067 compliant GHG inventory (Scopes 1-3)
2. Emission Reduction Planning
- Implement ISO 50001 energy management
- Renewable energy procurement
- Process electrification
3. Carbon Removal Strategy
- Nature-based solutions (reforestation, soil carbon)
- Technological removal (DACCS, BECCS)
4. Carbon Credit Procurement
- Source VCS/Gold Standard certified offsets
- Achieve PAS 2060-aligned neutrality
Seven Principles for Credible Net Zero

- Front-Loaded Reductions
Early deep cuts preserve climate options (each year’s delay reduces 1.5°C feasibility window by ~2 years) - Comprehensive Coverage
Address all GHGs across entire value chain - Carbon Removal Integrity
Use only for residual emissions after maximal reductions - Credible Offsetting
Select credits with verified additionality and permanence - Just Transition
Support developing economies through climate finance - Ecological Sustainability
Ensure solutions don’t compromise biodiversity - New Economic Models
Leverage $130T in climate-aligned capital
Strategic Advantages of Early Action

Policy Incentives:
- US Inflation Reduction Act ($370B in clean energy incentives) reduces implementation costs by 30-50%
Competitive Benefits:
- Preferred supplier status in regulated markets
- Enhanced brand valuation (up to 30% premium in some sectors)
- Access to green financing at preferential rates
Risk Mitigation:
- Avoidance of carbon tariff penalties
- Reduced exposure to physical climate risks





